Financial reporting is the bedrock of informed business decisions and stakeholder trust. It provides a systematic way for organizations to document and communicate their financial performance, position, and cash flows over a specific period. Through financial reporting, businesses can monitor their financial health, ensure compliance with regulatory requirements, and provide transparency to investors, creditors, and other stakeholders. High-quality financial reporting enhances the business’s credibility and facilitates strategic planning and resource allocation by providing accurate, timely, and relevant financial information.
What Is Financial Reporting?
Financial reporting involves preparing financial statements that present a company’s financial performance and position over a specific period. These reports include the balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement, and statement of changes in equity. For a deeper overview, see our Overview of Financial Reporting.
Why Is Financial Reporting Important?
Enhancing Transparency and Accountability
Financial reporting ensures that financial transactions and events are recorded and disclosed accurately. This transparency builds trust among investors, creditors, and other stakeholders by providing a clearer picture of the company’s financial health. For research on the topic, see Impact of Financial Reporting Transparency on Investor Decision-Making.

Supporting Informed Decision-Making
Accurate, timely financial reports help leaders make better strategic decisions. By analyzing financial statements, management can identify trends, assess performance, and plan for growth. See Key Financial Statements.
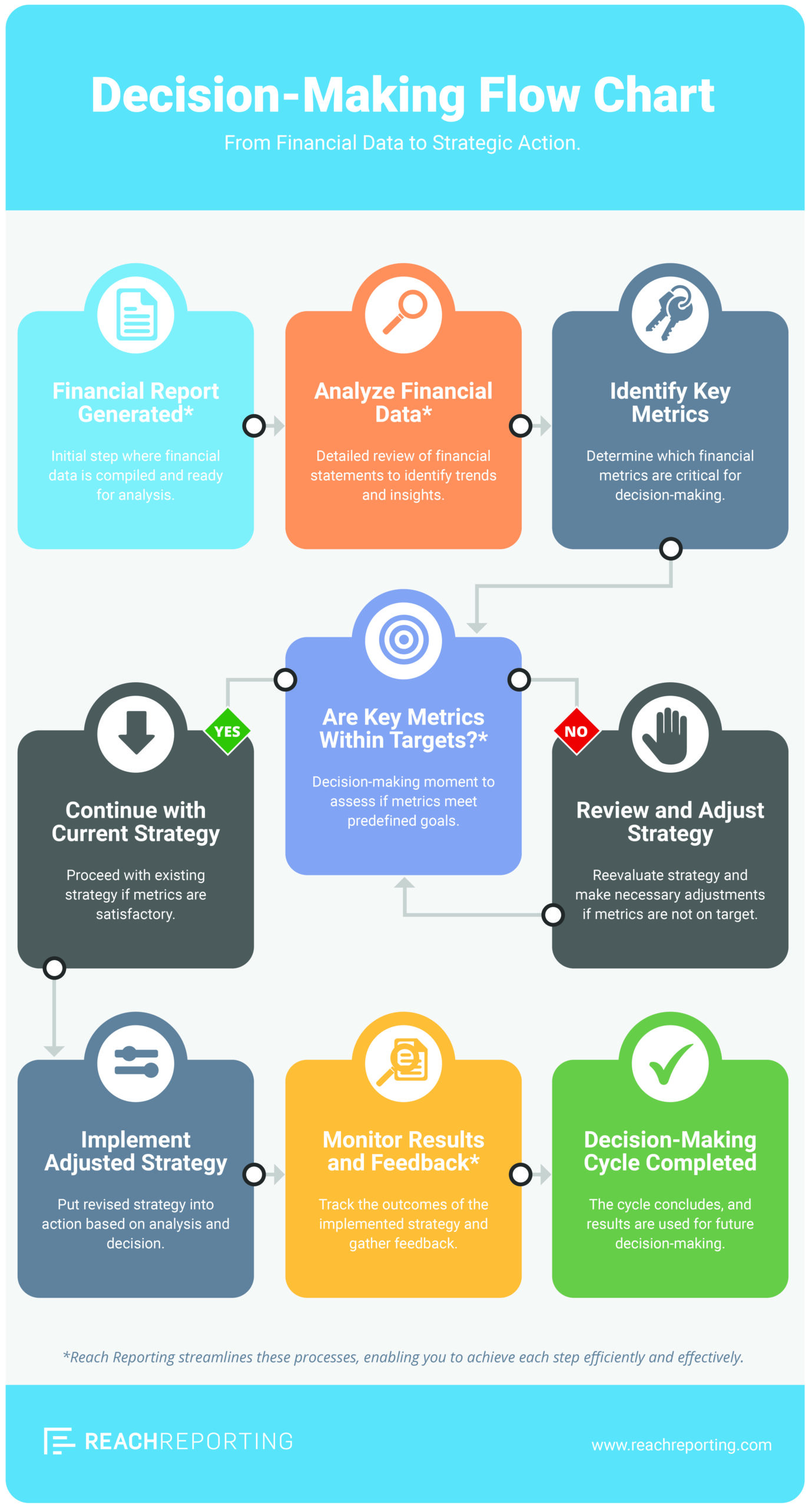
Facilitating Compliance With Regulations
Compliance with financial reporting standards and regulations, such as GAAP or IFRS, helps avoid penalties and supports consistent, comparable reporting.
Additional insight:
Attracting and Retaining Investors
Investors rely on financial reports to evaluate risk, performance, and viability. Clear, reliable reporting can attract new investors and retain existing ones by demonstrating stability and growth potential.
Enhancing Creditworthiness
Creditors and financial institutions use financial reports to assess creditworthiness. Strong reporting can improve access to financing and help secure better terms by demonstrating the company’s ability to manage and repay debt.
Improving Operational Efficiency
Detailed reporting helps identify inefficiencies and cost-saving opportunities. Financial reporting provides the data needed to streamline operations and optimize resource allocation. See Best Practices in Financial Reporting.
Enabling Performance Benchmarking
Financial reports enable benchmarking against industry standards and competitors, helping teams set realistic targets, identify strengths, and address weaknesses.
Supporting Tax Reporting and Planning
Accurate reporting supports tax compliance and planning by ensuring taxable transactions are documented and reported correctly, reducing the risk of errors and penalties.
Four Steps of the Financial Reporting Process
- Data collection — gather transactions, supporting documents, and account activity.
- Data processing — reconcile, classify, and standardize data.
- Data analysis — review trends, variances, and risks.
- Report generation — publish statements and distribute insights to stakeholders.
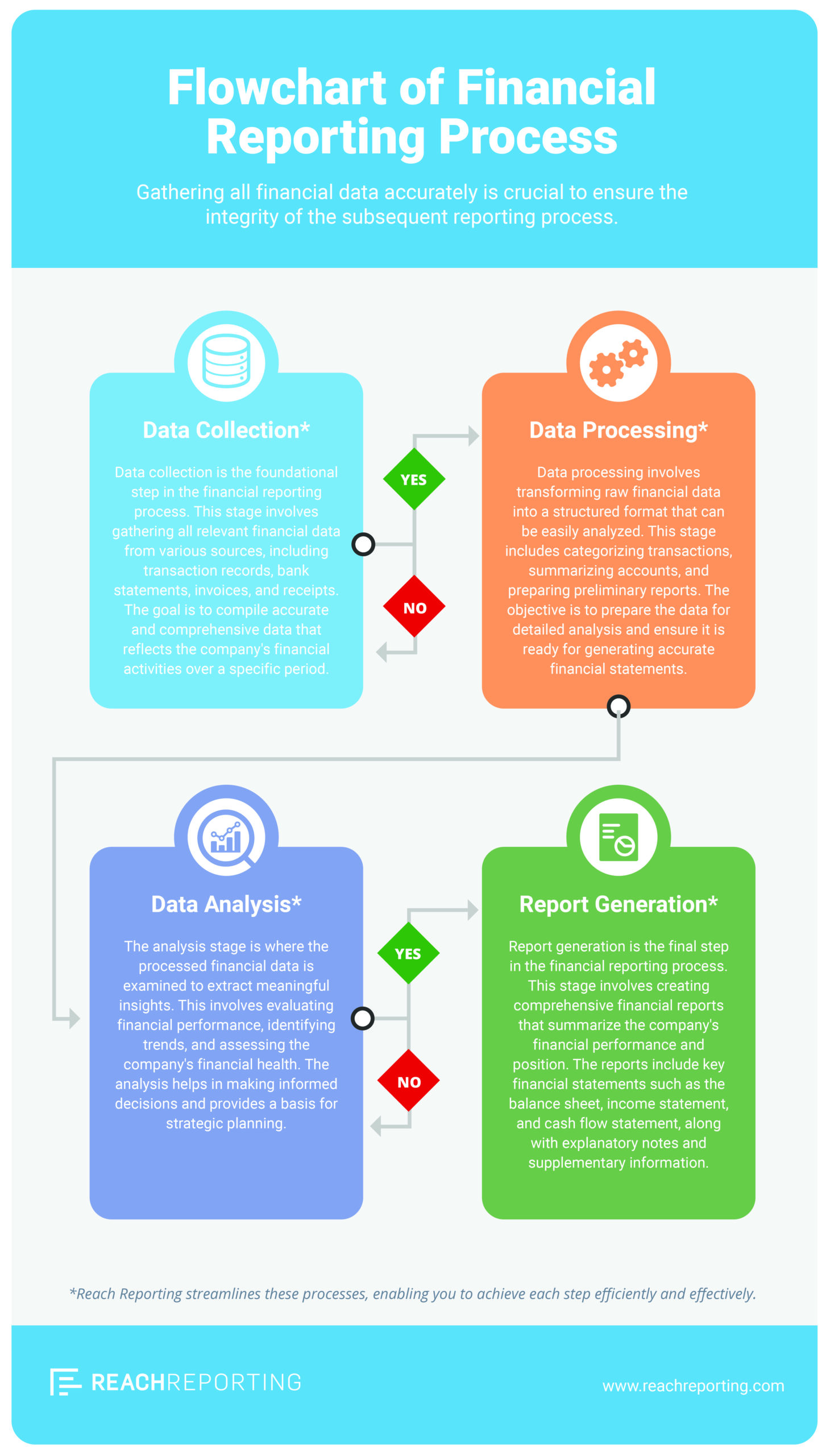
Additional insight:
- Overview of Financial Reporting
- Key Financial Statements
- Overview of GAAP
- Overview of IFRS
- Best Practices in Financial Reporting
- CFO’s Guide to Financial Reporting Techniques
- Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB): Official website
- International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS): Official website
- Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC): Official website
Conclusion
Financial reporting is not just a regulatory obligation, it’s a practical tool for business growth and resilience. Clear insight into financial performance supports stronger decision-making, transparency, and stakeholder confidence. Whether for compliance, investment, or internal management, effective financial reporting helps organizations navigate uncertainty and adapt in changing markets.
For more resources, visit Financial Reporting: The Ultimate Guide. If you have questions or need guidance, chat with us for support.
FAQ
This section answers common questions about the importance of financial reporting—from transparency and decision-making to frequency and consequences—so you can get quick clarity without digging through multiple sources.
Why is transparency in financial reporting important?
Transparency builds trust and confidence among stakeholders by demonstrating that financial practices are ethical, consistent, and reliable.
How does financial reporting help in decision-making?
Financial reports provide essential data that helps management make strategic decisions using accurate, timely information.
What are the consequences of poor financial reporting?
Poor financial reporting can lead to legal penalties, loss of investor confidence, and financial instability that jeopardizes the organization’s future.
How often should financial reports be prepared?
Most companies prepare financial reports quarterly and annually, though some businesses report more frequently based on operational needs or regulatory requirements.
What are the benefits of financial reporting?
Financial reporting helps track performance, improve decision-making, support compliance, attract investors, and plan for growth.
More Information
- Most Small Accounting Firms are Subject to the CTA’s BOI Reporting Rules — Wolters Kluwer
- Navigating Corporate Transparency Act / Beneficial Ownership Reporting — AICPA
- Strategies for Nonprofits to Ensure Public Support — Arizona State University Lodestar Center
- Maximizing Transparency: A Look at Financial Reporting — Deskera
- When and why does transparency matter for corporate social responsibility? — ScienceDirect
- Why Do Shareholders Need Financial Statements? — Investopedia

